Harnessing the Power of KPI Dashboards in Waste Management Centers
Waste management centers face increasing pressure to optimize their operations in the modern era of environmental consciousness and sustainability goals. Key Performance Indicator (KPI) dashboards have emerged as a vital tool in this quest for efficiency. By providing real-time data and insights into various aspects of waste management processes, these dashboards aim to address several critical challenges faced by the industry.
Challenges Addressed by KPI Dashboards
Waste management problems are multifaceted; they range from operational inefficiencies to regulatory compliance issues. KPI dashboards target these challenges head-on by tracking KPIs that help minimize the following hurdles:
Increased Waste Generation
The global population continues to grow, leading to higher waste volumes. Urbanization, consumerism, and industrial production contribute to this surge. Waste centers must cope with managing larger quantities of waste efficiently.
Complex Waste Streams
Modern waste includes diverse materials such as plastics, electronics, hazardous chemicals, and organic matter. Sorting and processing these varied waste streams demand advanced technologies and specialized knowledge.
Contamination
Contaminated waste disrupts recycling efforts. Mixing recyclables with non-recyclables or hazardous materials compromises the quality of recycled products. Waste centers struggle to educate the public and enforce proper disposal practices.
E-Waste
Electronic waste (e-waste) poses unique challenges due to its toxic components and rapid obsolescence. Proper disposal, recycling, and recovery of valuable materials from e-waste require specialized facilities and awareness campaigns.
Landfill Space Constraints
Finding suitable land for landfills becomes increasingly difficult. Waste centers must explore alternative disposal methods, such as waste-to-energy conversion, to reduce reliance on landfills.
Energy and Resource Recovery
Waste centers aim to extract value from waste. Technologies like anaerobic digestion, composting, and incineration can generate energy or recover materials. Balancing environmental impact and resource recovery is a delicate task.
Technological Advancements
Waste centers must stay abreast of technological innovations. Robotics, AI, and data analytics can enhance sorting efficiency, reduce costs, and improve overall operations.
Legislation and Compliance
Waste management regulations vary globally. Centers must navigate complex legal frameworks, monitor compliance, and adapt swiftly to changes. Non-compliance can result in fines and reputational damage.
Circular Economy Transition
The shift toward a circular economy emphasizes reducing waste, reusing materials, and extending product lifecycles. Waste centers must align their practices with circular principles to minimize environmental impact.
Public Awareness and Participation:
Educating the public about waste reduction, recycling, and responsible disposal remains a challenge. Waste centers need community engagement to foster sustainable behaviors.
Who is this Dashboard for?
The KPI dashboard is designed primarily for managers, supervisors, and decision-makers of waste management centers. These individuals need real-time insights to make informed choices, allocate resources efficiently, and drive continuous improvement in waste management practices.
Key KPIs in the Dashboard
The KPI dashboard should include the following essential KPIs and Metrics:
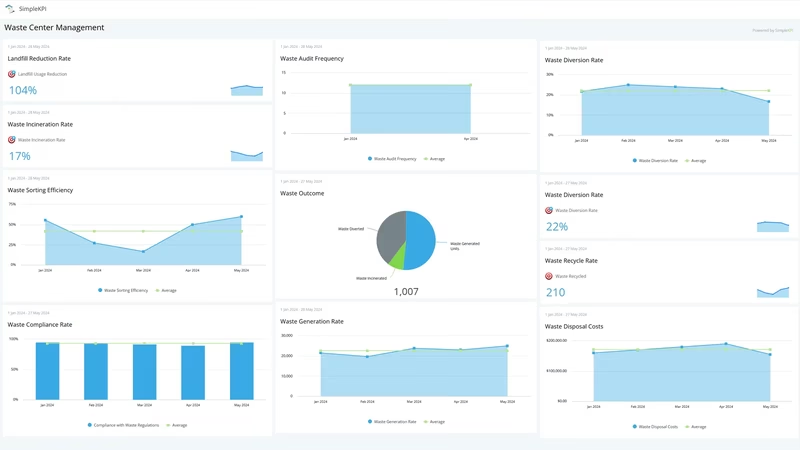
Waste Generation Rate
Calculated as the total waste generated divided by a specific time period (e.g., daily, monthly). It helps identify trends and plan capacity.
Recycling Rate
The percentage of waste diverted for recycling. A higher recycling rate signifies effective recycling programs.
Waste Disposal Costs
Monitoring costs associated with landfill disposal, incineration, or other waste treatment methods.
Waste Diversion Rate
Indicates the proportion of waste diverted from landfills. Higher diversion rates are desirable.
Waste Sorting Efficiency
Measures the accuracy and effectiveness of waste sorting processes.
Waste Incineration Rate
Tracks the percentage of waste incinerated. Balancing incineration with recycling is crucial.
Waste Audit Frequency:
Regular audits ensure compliance, identify inefficiencies, and improve processes.
Landfill Usage Reduction
Aims to decrease reliance on landfills by promoting recycling and other sustainable practices.
Compliance with Waste Regulations
Ensures adherence to environmental laws and regulations.
Waste Management Training Hours
Indicates investment in staff training and competence.
Carbon Emission Reduction:
Monitoring emissions associated with waste management activities.
Waste-to-Energy Efficiency
Evaluates the effectiveness of waste-to-energy conversion processes.